
When Pregnant, When Do You Get Your First Ultrasound?
A mother’s joy begins when new life is stirring inside, when a tiny heartbeat is heard for the first time, and a playful kick reminds her that
Oral sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, encompass a range of infections primarily transmitted through sexual activities involving the mouth. The transmission primarily occurs when one indulges in oral sex with an infected partner, facilitating the exchange of bodily fluids that carry the pathogens causing these diseases.
Oral STDs can have serious repercussions if left untreated, such as increasing the risk of sexually transmitted infection and causing poor oral health and long-term health complications. Some common oral STDs include herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
While some may not show symptoms or be easily treatable with antibiotics, others may have more severe consequences, such as HPV leading to throat or mouth cancer. Moreover, since these diseases can be transmitted without symptoms, it is crucial to use protection and get tested regularly.
Choices Women’s Clinic recommends that sexually active adults, especially those engaging in oral sex, be aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions. This blog will explain the importance of practicing safe oral sex and the various STDs that can be transmitted through this activity.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are a panoply of communicable diseases primarily spread through sexual intercourse. They are triggered by diverse pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites that infiltrate the body during intimate encounters. These microscopic invaders can cause many health problems–from mild and fleeting symptoms to chronic conditions with serious, life-altering consequences.
It is key to understand that while some STDs might present noticeable symptoms such as sores, pain, and unusual discharge, others might insidiously develop without any conspicuous signs, thus making them particularly treacherous. Regular testing, safe sexual practices, and open, informed dialogue with partners are, therefore, crucial in minimizing the potential risks of these diseases.
STDs function by taking advantage of the body’s natural processes. They are transmitted through sexual activity, which includes anal or vaginal sex and oral intercourse. These diseases can be passed from one person to another through direct contact with infected bodily fluids such as blood, semen, or vaginal secretions.
Some STDs can also be transmitted via skin-to-skin contact with infected areas or through sharing contaminated needles. Once inside the body, STDs use different mechanisms to survive and thrive, depending on the type of pathogen involved.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) function through intricate biological processes. At their core, they operate by breaching the body’s defense mechanisms, taking over host cells, and multiplying.
This process can be visually undetectable, making many STDs particularly dangerous due to their ability to remain unnoticed while causing substantial harm. The methodology of sexually transmitted disease and the subsequent biological interactions are complex, varying greatly depending upon the specific type of STD.
The transmission of STDs primarily takes place during sexual activity. The pathogens behind these diseases, whether bacterial, viral, or parasitic, are typically housed in bodily fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
During sexual contact, these microscopic organisms can transfer from one individual to another through microscopic tears in the skin or mucous membranes. Certain STDs, such as herpes and human papillomavirus (HPV), can also be passed through skin-to-skin contact even when no visible sores or warts are present, further complicating prevention efforts.
Once inside the new host, these stealthy pathogens begin the infection process. Many attach themselves to the host’s cells, injecting their genetic material. Other STDs, notably bacteria, operate differently.
Rather than infiltrating host cells, they multiply and spread in the space between cells. Regardless of their method, these pathogens essentially hijack the host’s cellular machinery for their reproduction, leading to an increase in their numbers and the subsequent onset of symptoms, if any.
The body’s immune system responds to these foreign invaders to neutralize them. This response can lead to inflammation, one of the common symptoms of many STDs. However, several STDs have evolved mechanisms to evade the immune system, enabling them to persist in the host’s body for extended periods.
HIV, for instance, targets and destroys specific immune system cells, gradually weakening the body’s defenses and leading to a state of immunodeficiency.
Many STDs function silently, causing damage without displaying obvious symptoms. Chlamydia, for instance, can lead to long-term complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility in women, often without any initial signs of infection.
Similarly, untreated syphilis can progress to affect the brain and heart over time seriously. This stealthy nature of many STDs underscores the importance of regular testing and early treatment.
Oral sex, also known as oral-genital contact, is a sexual activity that involves stimulating the genitals using the mouth, lips, or tongue. This can include fellatio (stimulation of the penis) and cunnilingus (stimulation of the vulva).
While it may not result in pregnancy, oral sex can transmit STDs such as herpes and gonorrhea. Practicing safe sex, including the use of barriers like condoms or dental dams, is crucial to prevent the spread of STDs through oral sex.
Oral sex involves using the mouth, lips, or tongue to stimulate one’s partner’s genitals. While it typically encompasses fellatio and cunnilingus, oral sex is not limited to these alone. The practice can be multifaceted, with various types involving different techniques and interactions. It is crucial to understand these distinct types, their practices, and nuances to ensure sexual health and satisfaction.
Fellatio, colloquially known as a blowjob, involves the oral stimulation of the penis. This act can be imbued with sensual tongue strokes along the shaft, gentle flickers around the crown, or rhythmic motion involving the entire mouth. The depth, pace, and pressure can be varied, engendering different intensities of sensation. It is a form of oral sex that can be performed solo as a part of foreplay or as the main sexual activity.
Cunnilingus, often called ‘going down’ on a woman, involves orally stimulating the vulva or the clitoris. This intimate act involves many techniques, from delicate licks to soft kisses, gentle nibbles, or rhythmic suction. The art of cunnilingus is profoundly centered on exploring one’s partner’s desires, taking cues from her reactions to tailor the act for her pleasure.
Anilingus, also known casually as ‘rimming,’ is the oral stimulation of the anus. This often misunderstood and stigmatized practice can bring about unique sensations due to the high concentration of sensitive nerve endings around the mouth, throat, and genital area. It involves gentle, exploratory licks, kisses, or caresses with the tongue around the outer rim or inside of the anus. Prior hygienic preparations, like a thorough wash, are vital for this practice.
The sixty-nine position, or ’69’, is a simultaneous act of oral sex wherein both partners stimulate each other orally. This act can be an intimate expression of reciprocity, where the giving and receiving of pleasure occur concurrently. It requires open communication and mutual consent to ensure comfort and satisfaction for both partners.
While fellatio, cunnilingus, anilingus, and the sixty-nine position remain the primary types, oral sex is not confined to these categories. The practice is as diverse as people’s sexual preferences and desires. It is essential to remember that any sexual activity, including different types of oral sex, should always involve explicit consent and be practiced safely to prevent the transmission of STDs.
Oral sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that can be transmitted through oral sexual activities such as fellatio, cunnilingus, and analingus. These include the STDs above and others like hepatitis B and HPV-associated mouth or throat infections.
Despite common misconceptions, engaging in oral sex does not guarantee safety from STDs. Many of these infections can be transmitted through oral contact with infected bodily fluids; some can even be spread through skin-to-skin contact. Therefore, it is essential to practice safe sex by using condoms or dental dams during oral activities.
Moreover, it is crucial to remember that STDs may not always present symptoms, particularly early. Regular testing is necessary for those who are sexually active, as early detection and treatment can prevent further spread of these diseases. Choices Women’s Clinic offers confidential and affordable STD testing and treatment services, including for oral sexually transmitted infections.
![]()
There are various types of oral sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), each with its own unique set of symptoms. Some common oral STDs include herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
These infections can be transmitted through oral-genital contact, and symptoms may include sores, ulcers, swelling, or unusual discharge in the mouth or throat. It is important to practice safe sex and get regular check-ups to prevent and detect oral STDs early on.
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that is often asymptomatic, hence its moniker as a ‘silent’ disease. Left untreated, this insidious pathogen can cause severe complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility.
Another bacterial STD, Gonorrhea genital herpes syphilis, human papillomavirus (HPV), presents discomforting symptoms like painful urination and unusual discharge. However, some individuals might experience no symptoms, making regular screening vital.
Syphilis, a multi-stage bacterial infection, can cause severe, long-term complications if not adequately treated. Often starting as a singular, painless sore, it can progress to systemic disease affecting the heart and the brain.
Herpes is a viral STD resulting in painful blisters and sores outbreaks. It has two types: Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1, primarily oral) and Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2, primarily genital).
HPV comes in many types, some of which can lead to genital warts or certain types of oral cancer. Notably, effective vaccines are available for some of the most harmful types of this virus.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a viral STD that damages the immune system and can lead to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). HIV specifically destroys CD4 T cells, which are crucial for immune response, leading to chronic immunodeficiency.
Preventions can be made to avoid contracting oral STDs. This includes practicing safe sex, getting regularly screened for STDs, and avoiding contact with the bodily fluids of an infected individual. Additionally, using barriers such as condoms or dental dams during oral sex can reduce the transmission risk. Overall, being aware of the risks and taking necessary precautions is crucial in preventing the spread of oral STDs.
Manifesting vigilance towards one’s health is paramount in preventing the transmission and spread of oral STDs. Regular screening tests, for instance, serve as an effective surveillance method in identifying asymptomatic infections. Early detection allows prompt treatment and significantly mitigates the risk of severe complications.
Vaccination is the cornerstone of preventative health care and is vital in curbing the spread of certain STDs. Health professionals around the globe highly recommend vaccines for HPV, Hepatitis A, and Hepatitis B. These vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight specific viruses, providing immunity against future infections.
Adopting safe sexual practices is an essential strategy for preventing STDs. Barrier methods such as dental dams during oral activity can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Avoiding risky sexual behaviors, such as having multiple sexual partners or engaging in unprotected sex, can lower the probability of contracting STDs.
Knowledge is the most potent weapon in the fight against STDs. Comprehensive sex education, which includes knowledge about STDs, their means of transmission, and prevention strategies, should be disseminated widely and repeatedly. With the right information, individuals can make informed decisions about their sexual health and lifestyle.
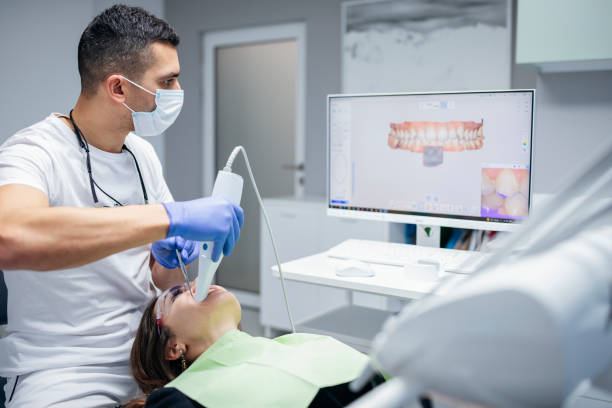
Regular dental check-ups can help in the early detection of oral STDs. Many STDs can cause lesions or other changes in the oral cavity that a dental professional can recognize. By scheduling regular dental visits, individuals can ensure that their oral health is monitored closely and any abnormalities are addressed promptly.
Communication with sexual partners about sexual health and STD status is crucial in STD prevention. It fosters mutual respect and understanding, allowing for informed decisions about sexual activities and safety precautions.
To summarize, preventing oral STDs is a multifaceted endeavor that requires education, vigilance, safe practices, open communication, and regular screening. By following these steps, individuals can take control of their sexual health and significantly reduce their risk of contracting STDs.
In conclusion, oral sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are primarily transmitted through oral-genital contact. They encompass various conditions, some of which can lead to serious health complications if not promptly addressed. However, their prevalence can be significantly curtailed with the judicious application of knowledge, vigilance, and proactive measures.
This involves comprehensive sex education, regular dental check-ups to facilitate early detection, the practice of safe sexual behaviors, and the establishment of open communication with sexual partners regarding sexual health. Through these concerted efforts, each individual can be decisive in the collective fight against oral STDs, safeguarding their health and communities.
Choices Women’s Clinic is committed to educating and empowering individuals with the information and resources to make informed decisions. Our comprehensive STD testing services provide a safe, confidential, and comfortable environment for individuals seeking peace of mind and proactive care.

A mother’s joy begins when new life is stirring inside, when a tiny heartbeat is heard for the first time, and a playful kick reminds her that

Carrying a baby is the most rewarding experience a woman can enjoy. But having a baby also comes with its challenges, including pregnancy insomnia. Pregnancy

At Choices Women’s Clinic, we understand the challenges that unexpected pregnancies can bring, and we are committed to providing a supportive environment for individuals facing

Boundaries are the psychological and emotional lines we draw between ourselves and others to ensure our safety, well-being, and happiness. Healthy sexual boundaries in a relationship

People usually use the terms STI and STD interchangeably, but there is a difference between them. STI stands for sexually transmitted infection, while STD stands

It seems like from the moment you learn about sex at a young age, the pressure to have sex is on. Whether you are single,
